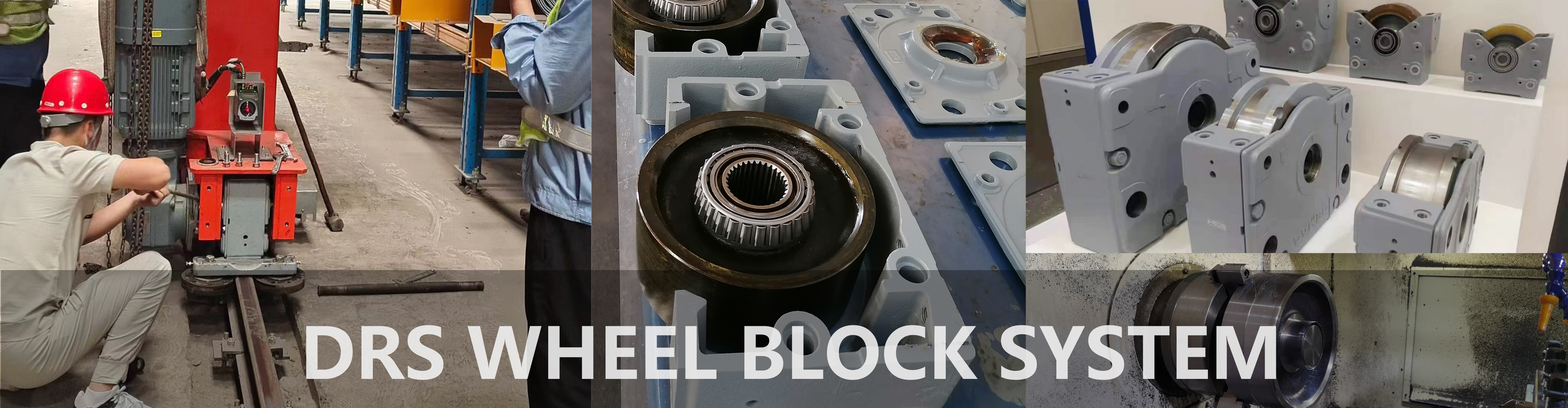
DRS Wheel Block System

DRS 200 Wheel Block with Side Connection (W-Type) Mounting
Maximize your crane's hook height and structural stability with the Demag DRS 200 Wheel Block with Side Connection (W-Type).
In the Demag DRS wheel block system, Side Connection is a critical installation design. Compared to Top Connection (K-type) or End Connection (E-type), it primarily addresses challenges related to spatial layout and structural load distribution.
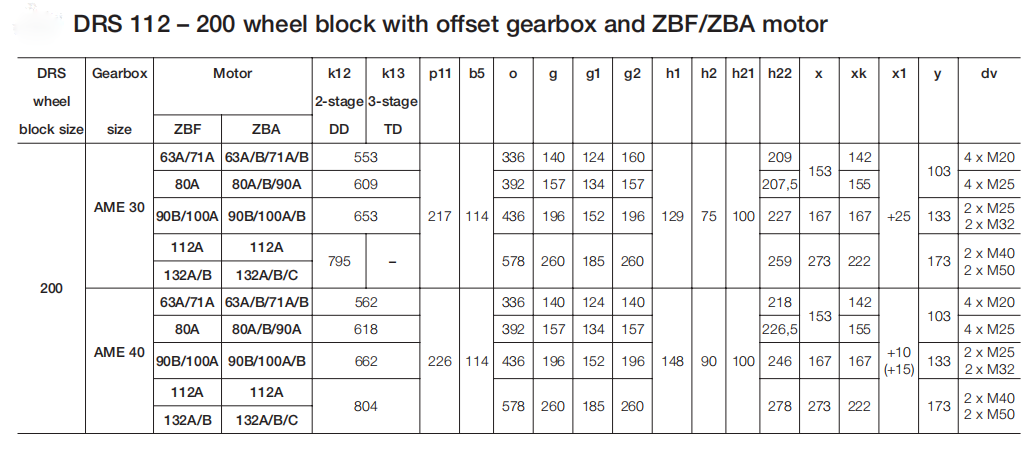
The following is an in-depth analysis of the Side Connection:
1. Structural Features: How is it connected?
Side Connection means that the side of the wheel block housing features pre-machined mounting holes.
Mounting Position: Instead of being suspended beneath the beam, the wheel block is "sandwiched" between two channels or fixed to the inner side of a plate-style structure.
Fixing Method: High-strength bolts are typically passed through the clearance holes of the support structure and screwed directly into the threaded holes on the side of the wheel block.
2. Core Advantages: Why choose Side Connection?
The selection of Side Connection is usually driven by three key factors:
Low Headroom: Since the wheel block is embedded or mounted alongside the structure, it does not occupy space beneath the beam. This is crucial for facilities with height restrictions where maximizing hook lift height is essential.
Higher Stability (Lateral Rigidity): The side connection integrates the wheel block into the load-bearing beam. This provides a larger support area and a more stable structure when handling lateral forces, such as swinging during crane starts/stops or lateral impacts from uneven rails.
Modular Flexibility: This method allows engineers to integrate the wheel block directly into complex mechanical frames without being limited to standard end carriage designs.
Technical Summary
Housing Material: High-quality die-cast aluminum (for the DRS 200 model), offering excellent geometric tolerances.
Installation Advantage: Side Connection allows for easy installation and maintenance from the side without dismantling the entire structure.
Adaptability: Compatible with various wheel tread forms (e.g., with flanges, flangeless, or non-slip polyurethane).
Drive Pairing: Typically paired with Demag offset gearboxes or right-angle gearboxes.
3. Comparison of Installation Types
Connection Type | Common Name | Mounting Features | Application Scenario |
Top (K) | Top Connection | Bolts inserted from above | Standard crane end carriages; simplest installation |
End (E) | End Connection | Bolts inserted from the longitudinal end | Ends of narrow, tubular structures |
Side (W) | Side Connection | Bolts tightened laterally from the side | Space-restricted, embedded designs, requiring high rigidity |
4. Maintenance and Replacement
For large wheel blocks like the DRS 200. Side Connection offers a significant maintenance advantage: lateral removal.
While Top Connection might require lifting the entire beam for replacement, a well-designed Side Connection allows the wheel block to slide out laterally simply by loosening the side bolts, greatly reducing downtime.
5. Application Examples
Telescopic Stackers: Due to extremely tight space requirements, wheel blocks are often side-loaded onto the telescopic arms.
Heavy-duty Transfer Carriages: To lower the platform height for easier vehicle boarding, wheel blocks are often hidden within the side frames of the platform.
Need a Solution? Contact Our Experts for Demag DRS 200 Side Connection Integration.